Autonomous deburring – The GOIMEK use case in focus
2 mins to read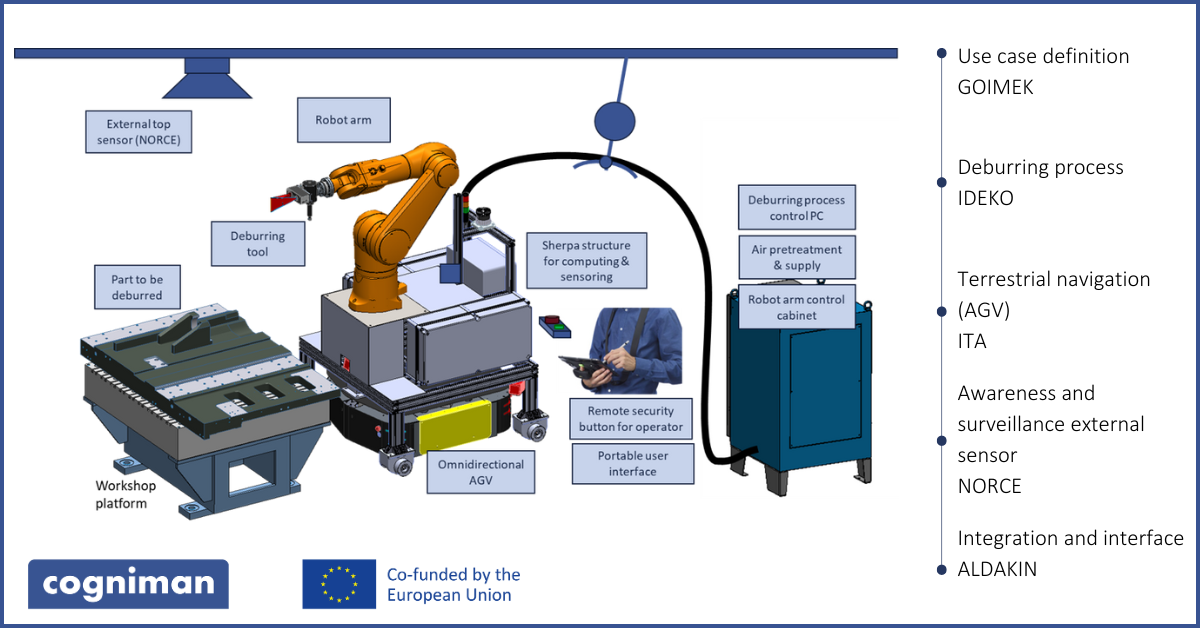
The GOIMEK use case within COGNIMAN focuses on deburring. In metal manufacturing, the deburring process is crucial in ensuring high-quality machined parts. Burrs, unwanted materials resulting from manufacturing, can lead to assembly or operational issues. This use case involves a thorough approach, including planning, developing robotic capabilities and integrating systems to monitor safety and quality.
Partners involved: Itainnova, IDEKO, Aldakin, NORCE and Montimage
Timeline for developing the solution for the GOIMEK use case
High-level requirements identified during the first year of COGNIMAN and the partner responsible for it
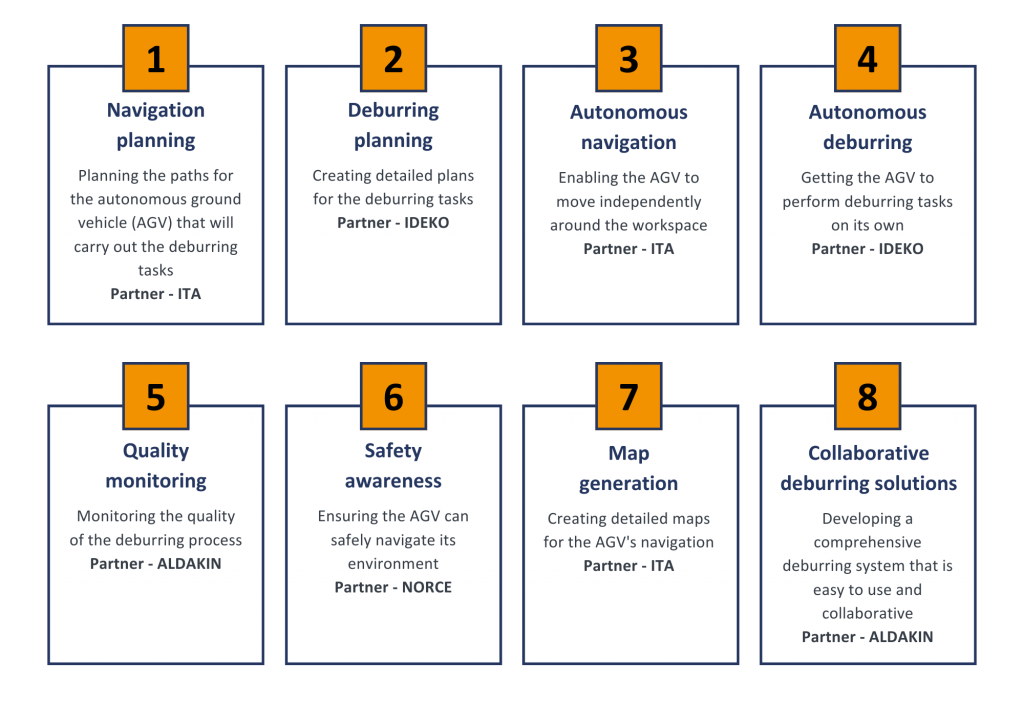
The use case involves several important steps, each essential for the successful execution of the deburring tasks:
- Part selection and pre-analysis: This initial step involves loading 3D models of the parts, detecting edges and selecting the appropriate edges for deburring.
- Deburring task planning: Setting parameters for deburring and generating paths for the deburring tools.
- Validation and mission upload: Evaluating the generated paths, coding mission programs and uploading them to the autonomous ground vehicle (AGV).
- Execution stage: The AGV navigates to the work area, the robot arm performs the deburring tasks and the AGV returns to its starting position.
- Review and feedback: The robot awaits operator review and feedback before returning to its charging dock.
Progress and developments
Over the past six months, significant progress has been made in connecting the robotic components to cloud-based systems, which allows for better data management and communication.
- Requirement 1 and 3 – Navigation planning and autonomous navigation: Using the software Nav2, the AGV plans and follows safe routes to the deburring positions.
- Requirement 2 – Deburring planning: Using CAD models, the data for deburring tasks is managed and the edges that need deburring are identified. This defines the deburring plan.
- Requirement 4 – Autonomous deburring: The robot and the 2D laser data create a 3D model of the part. A touch probe identifies the accurate location of the deburring part.
- Requirement 6 – Safety awareness: A physical robot mock-up uses synthetic training data to test the actual robot.
Potential stakeholders
Several stakeholders are identified as those who may be interested in an autonomous robot for deburring operations:
- Manufacturing companies: Companies producing metal, plastic, or other materials that require deburring may find value in improving efficiency, consistency and safety in their production processes.
- Industrial automation companies: Firms specialising in industrial automation may seek to develop or integrate autonomous deburring robots into their product offerings.
- End users: Automotive manufacturers, aerospace companies and medical device manufacturers, among others, may benefit from the improved quality and consistency provided by autonomous deburring robots.
In conclusion, the GOIMEK use case is making good progress by using advanced robotics, autonomous systems and collaborative technologies to improve manufacturing processes. The ongoing developments aim at enhancing efficiency and quality in industrial deburring.
Check out episode 2 of the COGNIMAN Conversations, where Arkaitz Aranburu from GOIMEK speaks about the use case.
